Threaded insert bushings press into components – Threaded insert bushings, indispensable components in various industries, offer a secure and reliable solution for creating strong, threaded connections in thin materials or components with limited space. This comprehensive guide delves into the design considerations, installation methods, quality control measures, and diverse applications of threaded insert bushings, providing a thorough understanding of their functionality and best practices for their effective utilization.
From selecting the appropriate bushing for specific applications to ensuring proper installation and maintaining long-term performance, this guide empowers readers with the knowledge and techniques necessary to harness the full potential of threaded insert bushings in their projects.
1. Introduction: Threaded Insert Bushings Press Into Components
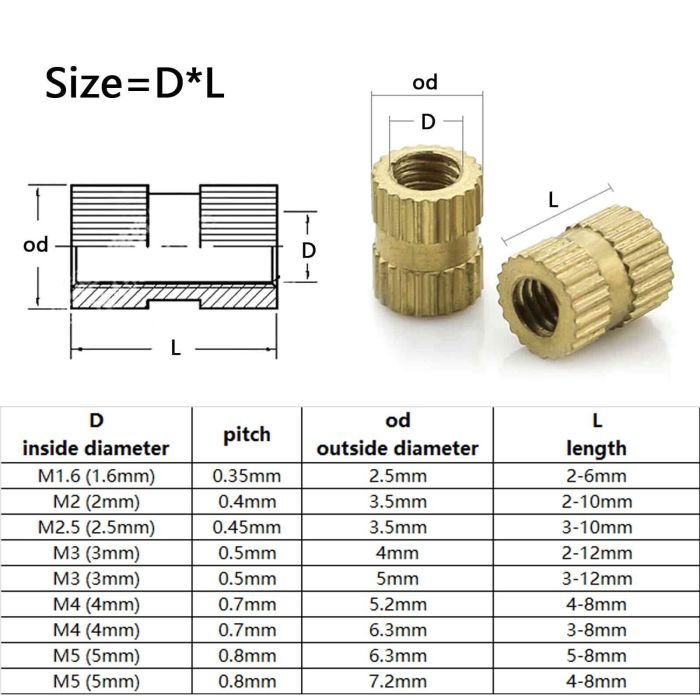
Threaded insert bushings are cylindrical inserts with internal threads that are pressed into components to provide a strong and reliable connection point for screws or bolts. They are commonly used in applications where a strong and permanent thread is required in a thin or soft material, or where frequent assembly and disassembly is anticipated.
Threaded insert bushings are available in a variety of materials, sizes, and thread types to suit different applications. They are typically made of brass, steel, or stainless steel, and can have a variety of thread types, including metric, inch, and Unified National Coarse (UNC) threads.
2. Design Considerations
When selecting a threaded insert bushing for a specific application, several factors should be considered, including:
- Material:The material of the bushing should be compatible with the material of the component into which it will be pressed. Brass bushings are commonly used for general-purpose applications, while steel bushings are used for high-strength applications. Stainless steel bushings are used for applications where corrosion resistance is required.
- Size:The size of the bushing should be appropriate for the size of the screw or bolt that will be used. The bushing should be large enough to provide sufficient thread engagement, but not so large that it weakens the component.
- Thread type:The thread type of the bushing should match the thread type of the screw or bolt that will be used. Metric threads are commonly used in Europe and Asia, while inch threads are commonly used in the United States.
3. Installation Methods
Threaded insert bushings can be pressed into components using a variety of methods, including:
- Manual press:A manual press is a simple and inexpensive tool that can be used to press threaded insert bushings into components. Manual presses are available in a variety of sizes and capacities, and can be used to press bushings into a wide range of materials.
- Hydraulic press:A hydraulic press is a more powerful tool than a manual press, and can be used to press threaded insert bushings into harder materials. Hydraulic presses are available in a variety of sizes and capacities, and can be used to press bushings into a wide range of materials.
- Ultrasonic welding:Ultrasonic welding is a process that uses ultrasonic waves to generate heat and pressure to bond two materials together. Ultrasonic welding can be used to press threaded insert bushings into components made of plastic or other soft materials.
4. Quality Control
Quality control is essential when installing threaded insert bushings. Proper installation ensures that the bushing is securely fastened in the component and will not loosen or fail under load.
Several inspection techniques can be used to ensure proper installation, including:
- Visual inspection:A visual inspection can be used to check for any obvious defects in the bushing or the installation. The inspector should look for cracks, burrs, or other damage that could affect the performance of the bushing.
- Torque testing:Torque testing can be used to measure the torque required to tighten a screw or bolt into the bushing. The torque should be within the specified range for the bushing and the screw or bolt.
- Pull testing:Pull testing can be used to measure the force required to pull a screw or bolt out of the bushing. The pull force should be greater than the specified pull-out force for the bushing.
5. Applications
Threaded insert bushings are used in a wide variety of industries and applications, including:
- Automotive:Threaded insert bushings are used in automotive applications to provide strong and reliable connection points for screws and bolts in a variety of components, including engine blocks, transmissions, and suspension systems.
- Aerospace:Threaded insert bushings are used in aerospace applications to provide strong and reliable connection points for screws and bolts in a variety of components, including aircraft engines, landing gear, and control systems.
- Electronics:Threaded insert bushings are used in electronics applications to provide strong and reliable connection points for screws and bolts in a variety of components, including printed circuit boards, connectors, and enclosures.
6. Troubleshooting
Several common problems can occur during the installation or use of threaded insert bushings, including:
- The bushing is not properly seated in the component:This can occur if the bushing is not pressed into the component far enough, or if the component is not properly prepared for installation.
- The bushing is loose:This can occur if the bushing is not properly tightened, or if the component is not properly prepared for installation.
- The bushing is stripped:This can occur if the bushing is overtightened, or if the screw or bolt is not properly tightened.
User Queries
What are the primary advantages of using threaded insert bushings?
Threaded insert bushings provide several advantages, including increased strength and durability of the joint, improved thread engagement, reduced risk of thread stripping or damage, and the ability to create threads in thin or fragile materials.
How do I select the right threaded insert bushing for my application?
Selecting the appropriate threaded insert bushing involves considering factors such as the material and thickness of the component, the required thread size and type, the expected load and torque requirements, and any environmental or temperature constraints.
What are the key steps involved in installing threaded insert bushings?
The installation of threaded insert bushings typically involves preparing the component by drilling a pilot hole, inserting the bushing into the hole, and pressing or swaging the bushing into place using a hydraulic or mechanical press.
How can I ensure the quality and reliability of threaded insert bushing installations?
Quality control measures for threaded insert bushing installations include visual inspection, dimensional verification, torque testing, and non-destructive testing methods such as ultrasonic or eddy current testing.
What are some common troubleshooting tips for threaded insert bushing installations?
Common troubleshooting tips include addressing issues such as misalignment during installation, insufficient press force, or damage to the bushing or component. Proper preparation, careful installation, and regular maintenance can help prevent these problems.